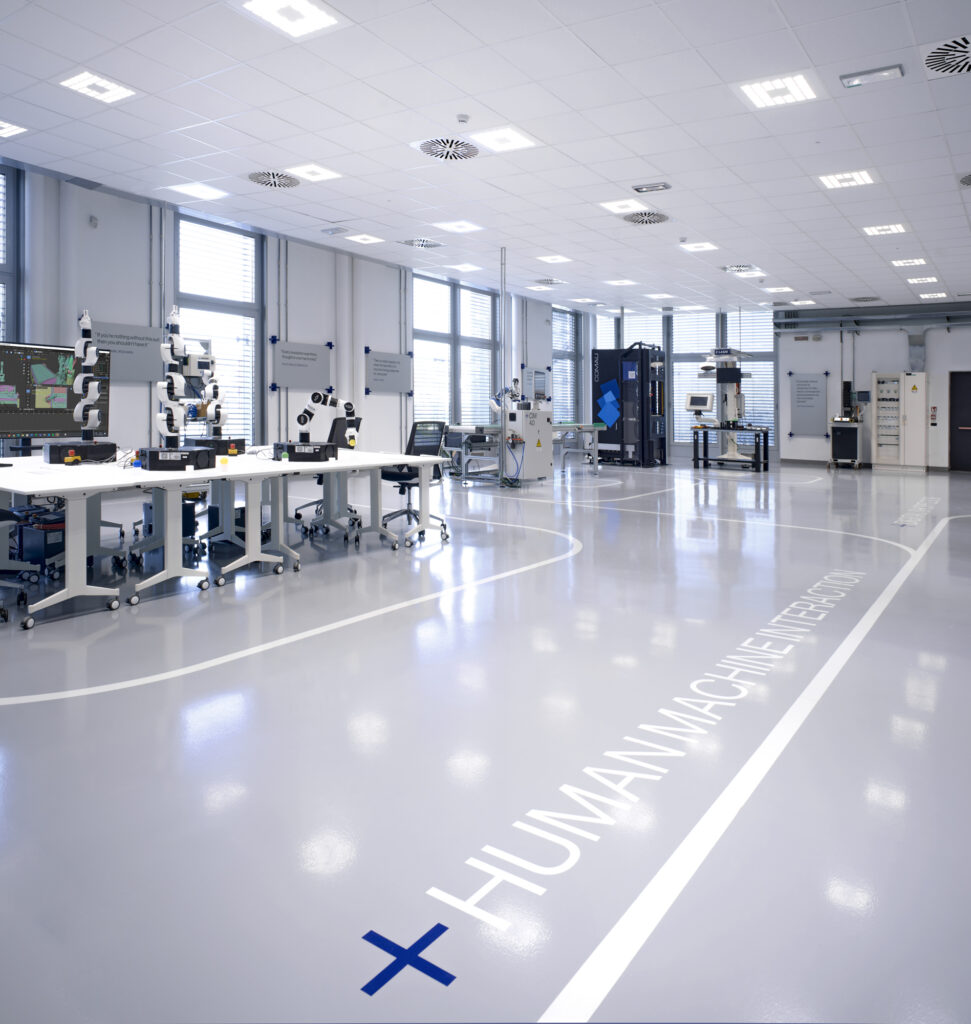
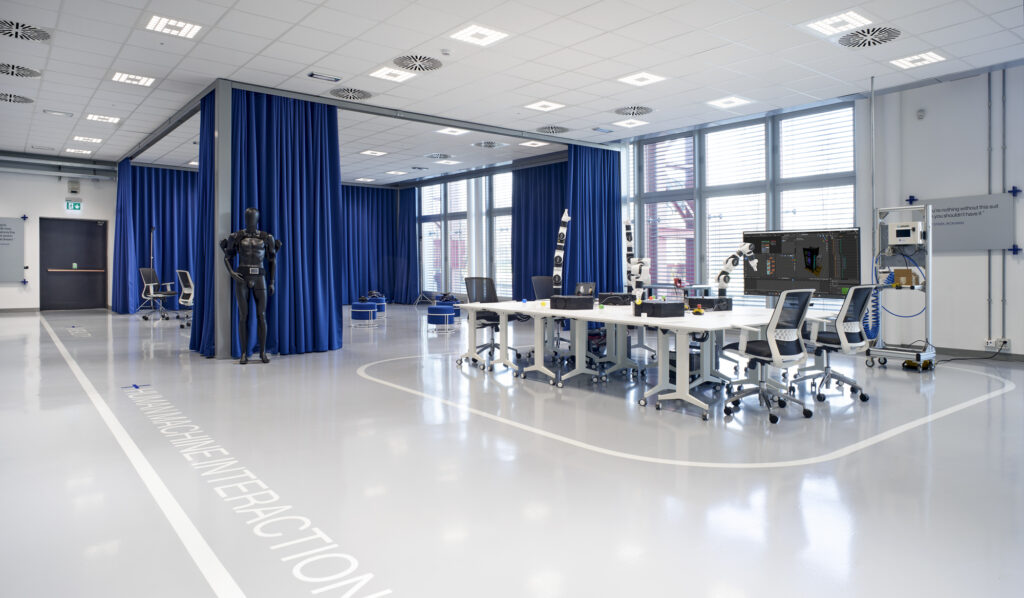
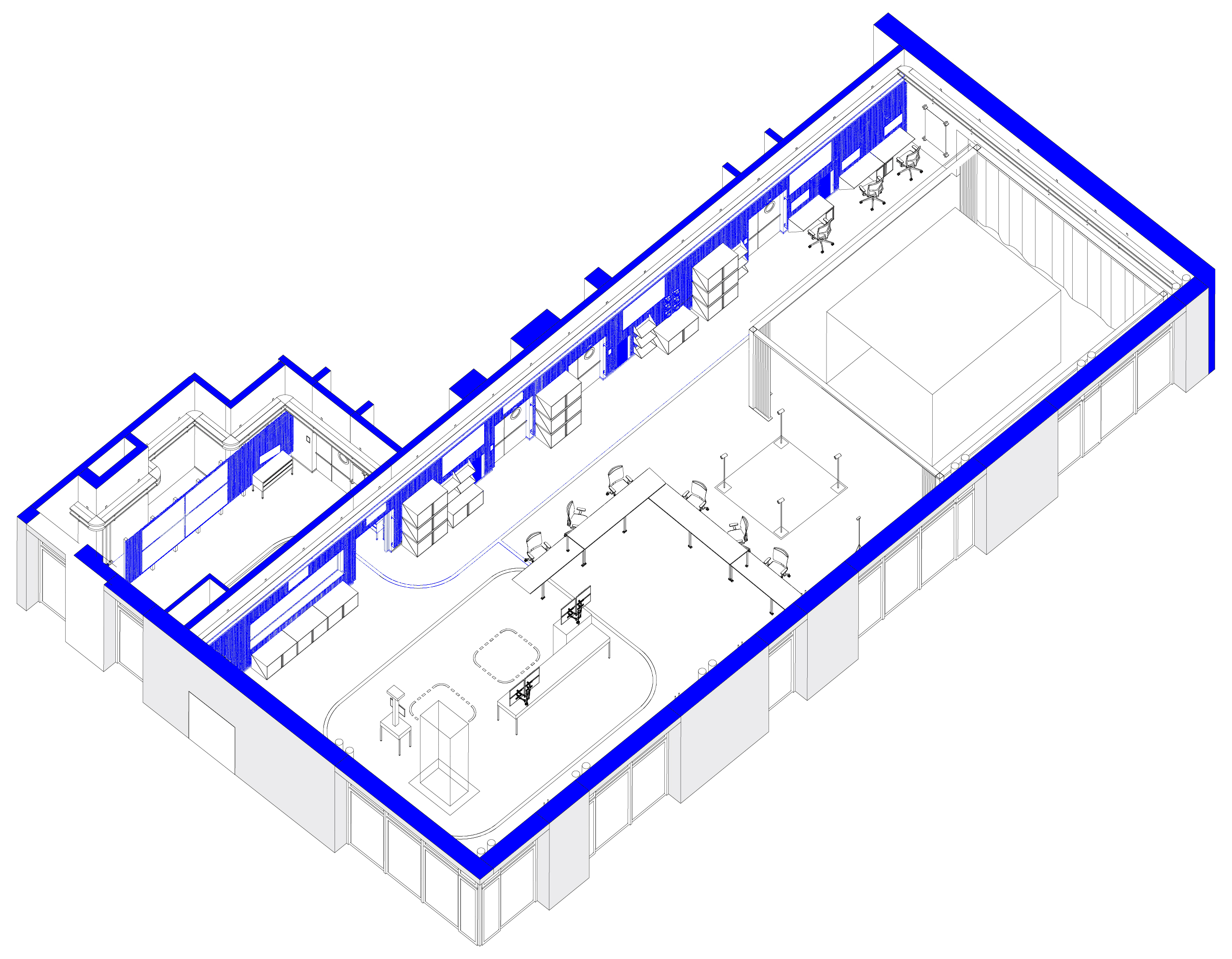
Digital Factory Pilot Line
The pilot line dedicated to digital factory technologies. The place where enterprises can explore digital technologies that can increase production efficiency and business competitiveness.
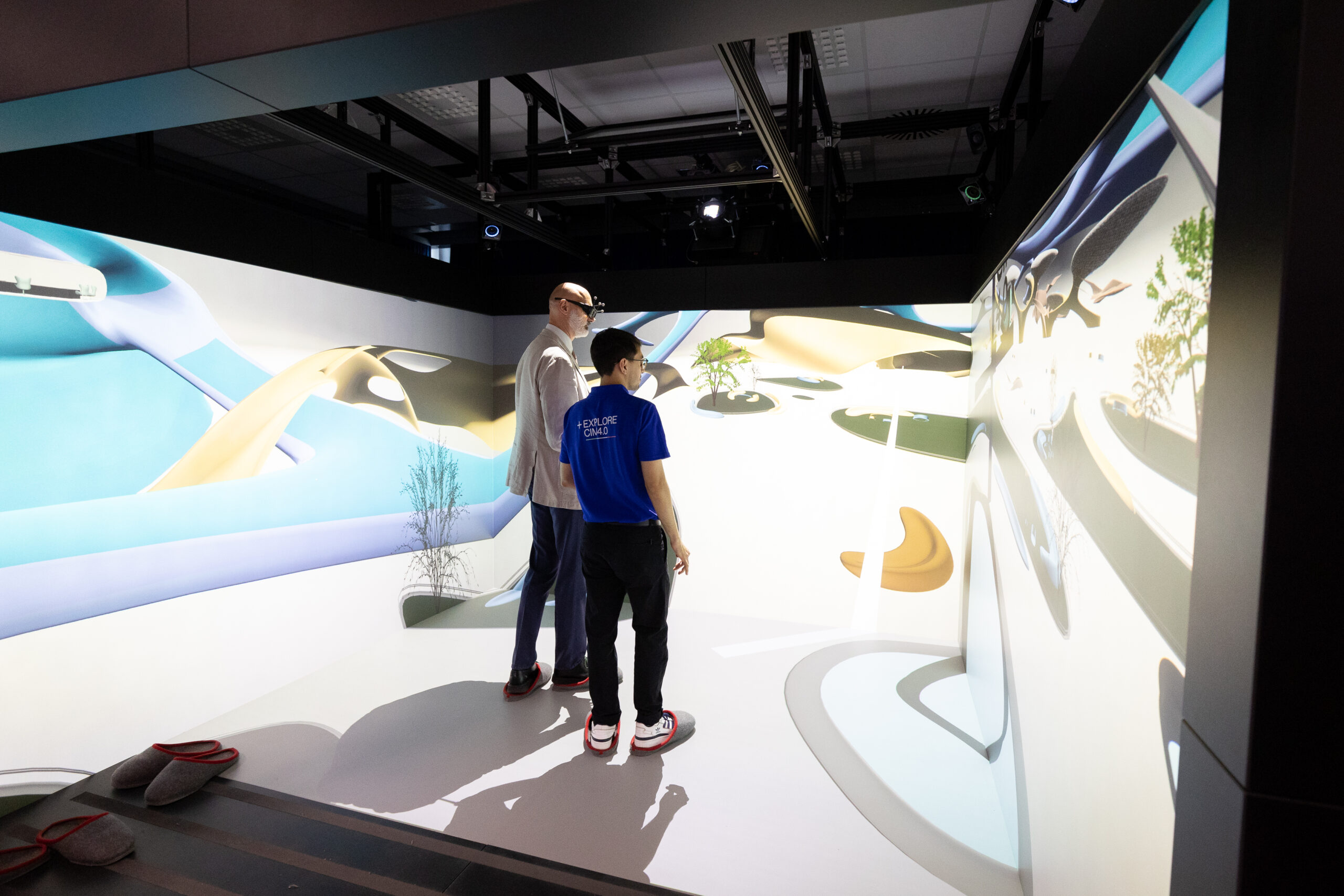

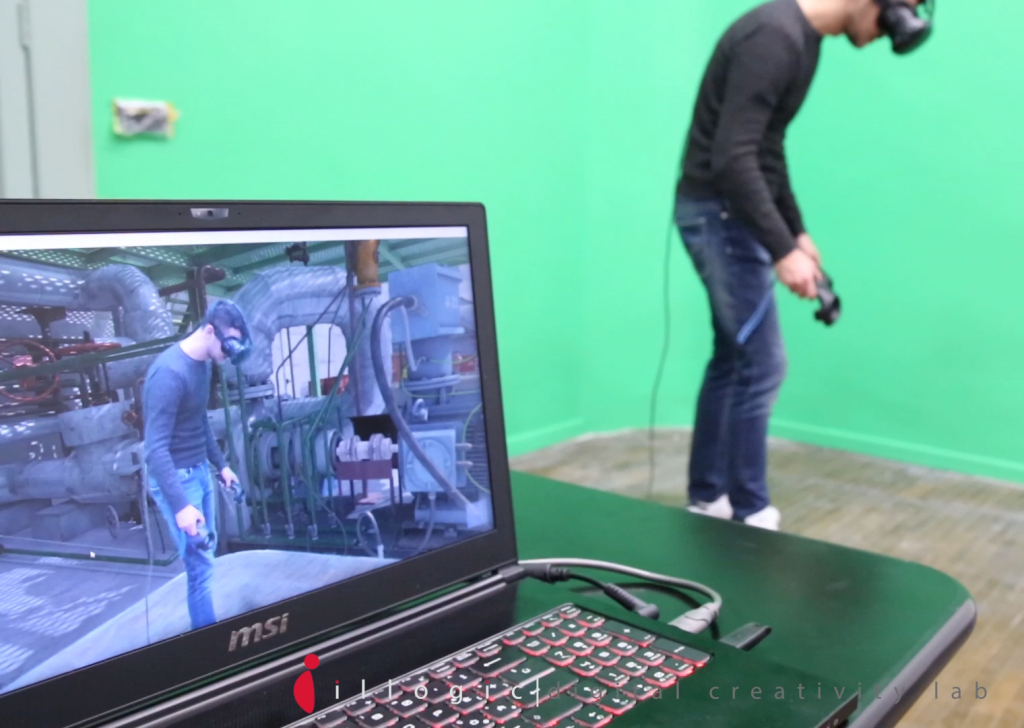
Visit the pilot line in VR
The Digital Factory is waiting for you in virtual reality
Expertise
Digitization is within everyone’s reach, Large Enterprises and SMEs. We have the expertise to support businesses, speaking their language.
We support companies starting from the opportunity analysis stage to understand the need for innovation from a technological and business perspective. We help in defining an implementation strategy by involving technical managers and interacting with operational figures in companies. We support the launch of pilot projects by bringing technologies into the prototype production environment, where KPIs and cost-effectiveness can be assessed to be associated with planned investments. Execution of the long-term strategy is the last step in view of defining the business plan and turning experiments into full-time services.
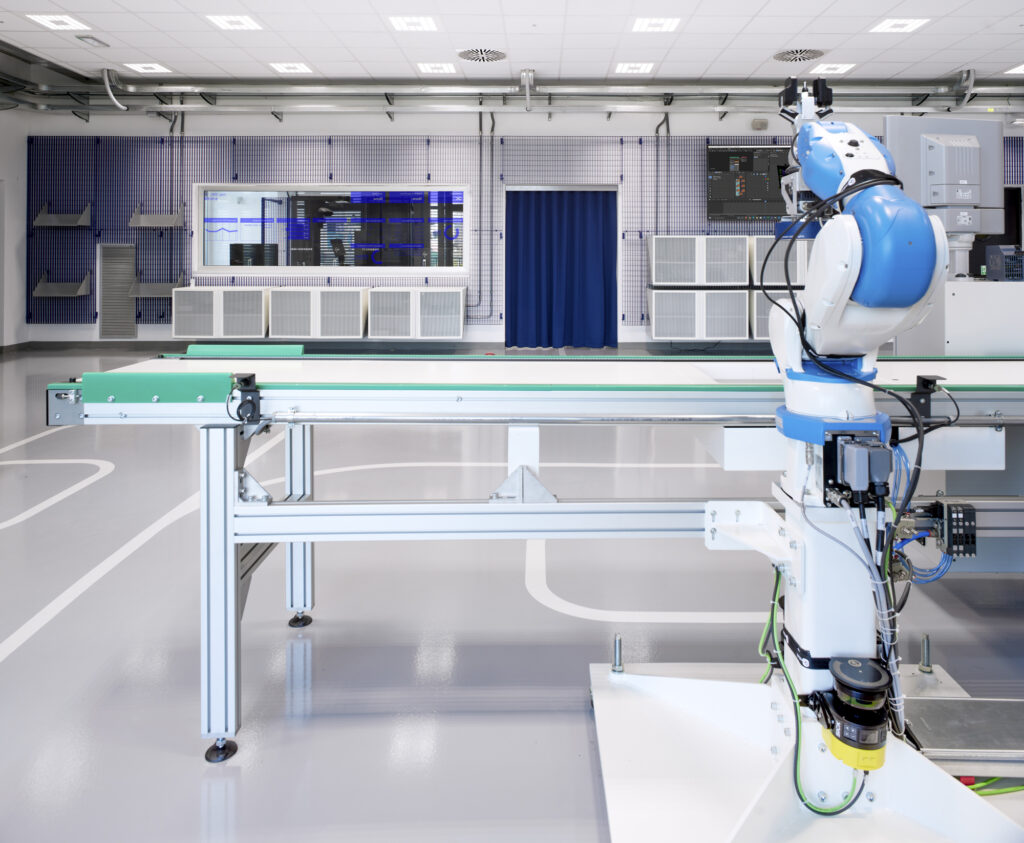
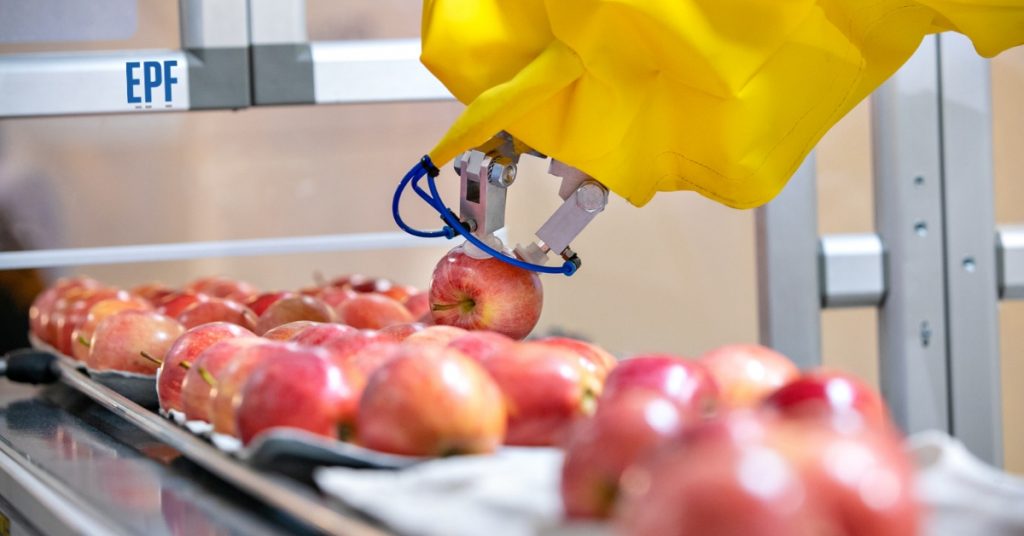
Advanced Robotics
Advanced robotic systems enable the transformation and redesign of industrial operations. Today it is possible to take advantage of high security mechanisms and flexible integrability features. These are collaborative robots that interact with operators, providing all-around safety by avoiding barriers to protection. Robots can be integrated into virtual environments and tested before commissioning.
Distributed Intelligence
Distributed intelligence systems are based on the use of cooperative systems organized into hardware or software components that independently handle specialized tasks. Industrial Edge enables real-time pre-processing of data produced by sensors applied to machines and devices, merging industrial IoT data with operational data. Companies can take advantage of a cloud system in which to extensively process aggregated data, perform critical actions, and develop AI-based business intelligence logic.
Extended Reality (XR)
XReality (XR) represents augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR) and mixed reality (MR) technologies, which are now being applied in various industries such as training, security and simulation. With commercially available hardware, the manufacturing industry has seen an increase in the use of XR technologies, shortening the gap between 3D modeling and virtual environment creation. Tools such as holographic viewers and smart glasses are useful for designing virtual simulation and training environments, augmented operator functionality, and solutions that also impact the business paradigm itself.
Cyber Security & Privacy
The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies brings cyber risks to the entire business. Due to the interconnectedness of technologies, cyber threats are frequent and expose people, tools, processes and intellectual property to high risk. In the past, cybersecurity aimed to prevent connections between outside and inside the work area; today, with cloud-connected machines, cybersecurity aims to provide comprehensive IT/OT protection.
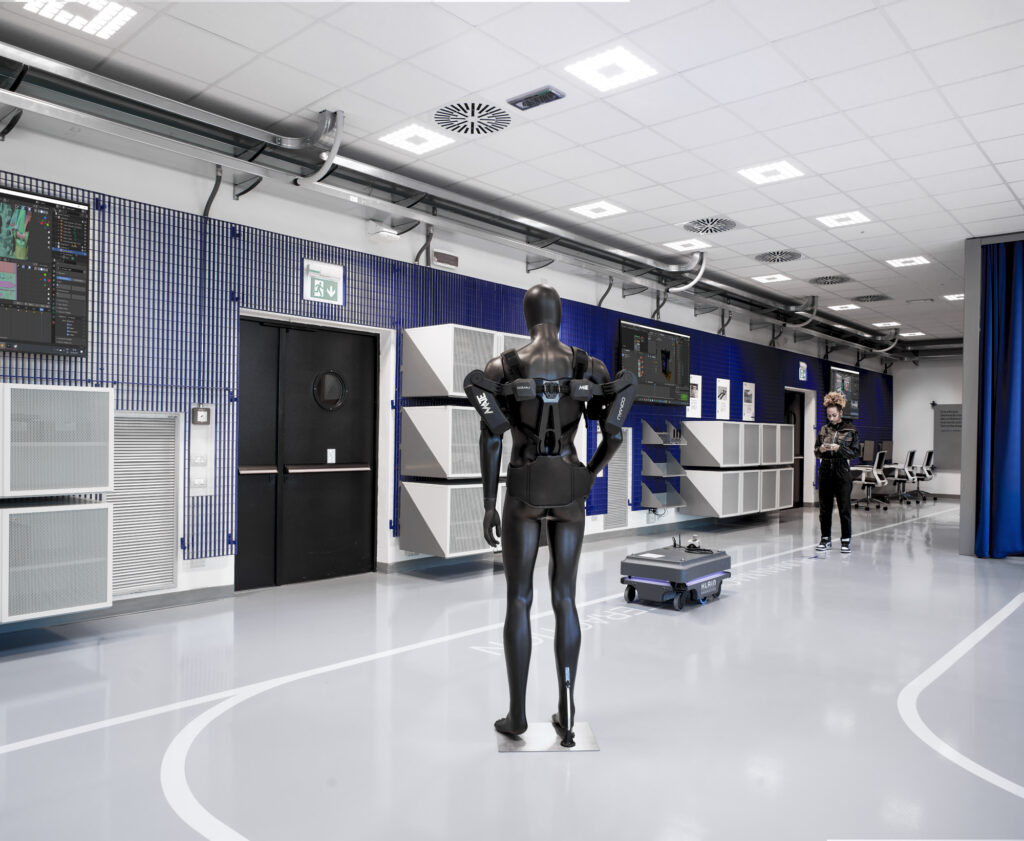
Flexibility, Ergonomics & Safety
Lean Production and World Class Manufacturing are methodologies that companies adopt to increase their production efficiency. Digital technologies support the adoption of these practices both at the process design and management stage and at the operational level.
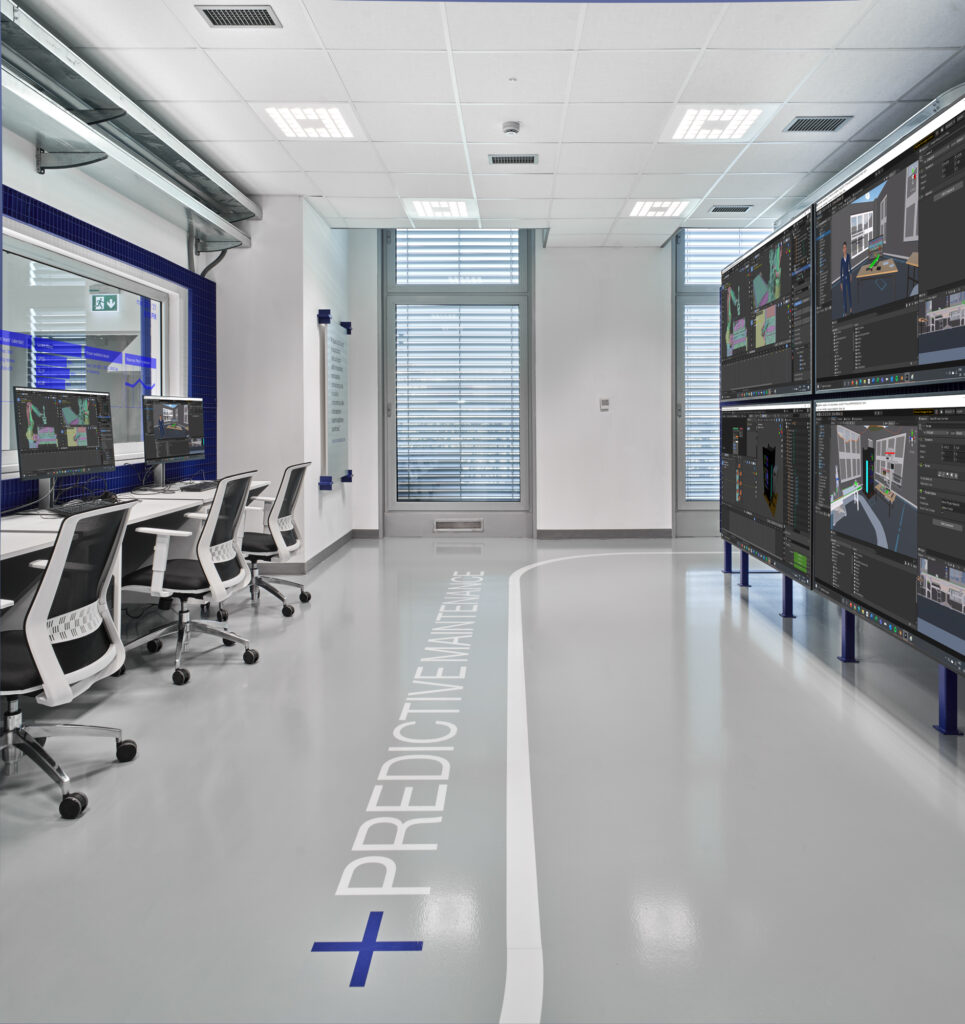
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance uses data analysis tools and techniques to detect equipment anomalies and defects in order to fix them before an actual failure occurs. Predictive maintenance can reduce the frequency of maintenance services, preventing unplanned repairs and costs. However, it requires the establishment of a complex plan that addresses information security policies and data acquisition, aggregation and management, as well as an appropriate user interface to support operators.
Next Generation Network
The concept of next-generation networks is based on enabling extended and distributed broadband networks. Incoming mobile wireless connectivity, such as 5G and WiFi6, will increase connection speed, improve battery life, increase network capacity, and expand bandwidth compared to previous networks. Regarding Industry 4.0 technologies, it will facilitate the adoption of ultra-low power, low latency IoT sensors for improved XR and real-time location services (RTLS).
Digital Retrofitting
Adopting Industry 4.0 technologies means identifying and applying the right available COTS digital technologies. It involves studying brownfields and company-specific needs, avoiding redesigning equipment or purchasing expensive or obsolete equipment. It is about assessing value added, because production efficiency is the driver for facing competition.
CIM4.0 WEDGE HUB
Extension of the pilot line, the new Innovation Hub in the Province of Cuneo inside the Michelin plant. An innovative space that aims to provide support to manufacturing companies in the area on the digitalization of industrial processes.
Visit the page
Our spaces